
Cloud Computing 101: Understanding the Basics
Table of contents
In the age of digital transformation, cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses operate and deliver their online services. Many of the apps we use every day rely on powerful infrastructures that are deployed in the cloud.
But even though cloud computing is all around us, it remains an enigma for many. This article will explain what cloud computing is by covering essential aspects such as its definition, key types, infrastructure models, and deployment strategies.
Whether you're new to the concept or an enthusiastic learner, this article will lay the groundwork for a clearer comprehension of the cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing resources such as servers, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence whenever you need them over the internet without the need of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers. And the best part? You pay for only what you use.
Unlike the traditional computing, these resources are dynamically assigned and reassigned among multiple users and can easily adjust to meet each user's demands.
It's all about being flexible and adapting to what you need, when you need it.
History of cloud computing
Cloud computing has evolved over decades, originating with mainframe computers in the 1950s and 1960s. However, the term "cloud computing" itself gained popularity in the early 2000s. Here's an overview of the history:

- 1950s: Organizations rented mainframe computation time, allowing remote access via terminals for multiple users, which established the foundation for shared computing resources.
- 1970s: The rise of virtualization, a technology that enables the creation of multiple virtual machines from a single physical computer, which laid the groundwork for the cloud's scalable resources.
- 2000s: AWS's launch in 2002 marked the commercialization of cloud computing, offering storage, computing power, and databases, fueling widespread adoption.
- 2010s: Cloud computing saw explosive growth, embraced by businesses for scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility. Major providers like Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud offered diverse services to cater to various needs.
In general, the origins of cloud computing can be traced back to the mainframes of the 1950s. Technologies like virtualization and hypervisors played a key role in shaping today's cloud computing landscape.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services and resources are provided in a variety of ways allowing different levels of support and flexibility in terms of hardware, maintenance and software.
The services provided by the cloud fall into one of these three primary categories:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It includes services like virtual machines, storage, and networking.
Users have more control over the infrastructure and can manage applications, data, middleware, and operating systems.
Examples include AWS EC2 and Azure VMs that Provide scalable virtual machines in the cloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the complexity of infrastructure management.
PaaS includes tools, development environments, and middleware needed to build, test, deploy, and maintain applications.
Examples include Google App Engine which enables building and hosting web applications on Google's infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications directly without needing to install, manage, or maintain the underlying infrastructure.
Examples include email services, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and office productivity suites like Google Workspace (GSuite).

Choosing the right type depends on how much control you want over your resources. Each type of cloud service model has its own advantages and is suitable for different business requirements, depending on factors like scalability, control, cost, and complexity.
Cloud Deployment Models
You might have heard the term "cloud deployment model" thrown around, but what does it actually mean? It's all about where your infrastructure lives, who's in charge, and how you access everything. Think of it like different types of apartments in the digital world.
There are three main deployment models to choose from, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks:
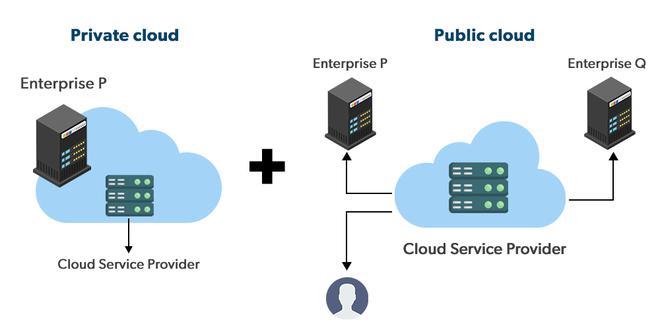
Public Cloud
This deployment model involves infrastructure and services provided by a third-party cloud service provider, available for use by the general public over the internet.
It's like a lively co-living space. You share resources with others, it's affordable and easy to move in, but you might have less privacy and control.
Private Cloud
In contrast, a private cloud involves dedicated infrastructure exclusively accessible by a single organization. This model may be managed either by the organization itself or by a third-party service provider.
It's like your own digital penthouse. You have the keys, the fancy furniture, and complete control. Perfect for secret projects or sensitive data storage, but it's also expensive, requiring significant investment in hardware, software, and personnel.
Hybrid Cloud
This model combines elements of both public and private clouds. The hybrid cloud model integrates distinct cloud environments, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
It's like having both! You've got your secure apartment for important stuff and a shared co-working space for everyday tasks. You can switch back and forth easily, keeping costs down and privacy high.
Tradeoffs of cloud computing
While cloud computing offers advantages such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, it also comes with a distinct set of compromises. Here's a breakdown of the major ones:
- Cost: unpredictable costs due to variable usage and potential vendor lock-in, making cost optimization crucial.
- Security and Privacy: entrusting data to a third-party provider raises concerns about data breaches, compliance issues, and the possibility of government access.
- Downtime and Reliability: despite its benefits, cloud services can still experience outages, impacting essential operations. Dependence on internet connectivity also introduces vulnerabilities that must be addressed.
- Sustainability: cloud's energy consumption raises environmental concerns, requiring consideration of providers' green credentials.
Ultimately, the decision to adopt cloud computing requires a careful evaluation of these trade-offs in alignment with your specific needs, priorities, and risk tolerance.
Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all answer. The ideal balance between cloud and on-premise solutions will vary depending on your unique circumstances.
Takeaways
This post is part of a series where I explain topics related to cloud computing. Here's what you can take away from this one:
- Cloud computing is like renting someone else's computers, internet connection, and storage space over the internet.
- The introduction of hypervisors (virtualization) marks an important point in the evolution of cloud computing.
- There are different types of cloud services based on how much the provider manages for you: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS etc.
- The cloud provides options for deploying apps/infrastructure: publicly in shared resources, privately, or in a hybrid mode combining both.
- Despite its advantages, cloud computing has many tradeoffs we have to consider before deciding to use it.
Conclusion
Cloud computing isn't just about using someone else's computer. It includes lots of different services on a large scale. One of these services is storage, which includes files, objects, and databases.
In the upcoming post, we will delve further into storage as a specific cloud computing service, discussing different types as well as when and how to use each type effectively.
If you have any questions, suggestions or need further clarifications, please feel free to get in touch with me. I'm here to help and support your journey in any way I can ^_^.
